CBD is a compound that has surged in popularity in the past decade. You can find CBD sodas, lotions, vapes, supplements, and more these days. But without an understanding of CBD, it's hard to know which products to buy — if any.
Learn about CBD, its benefits and side effects, and what to look for when purchasing a high-quality and trusted CBD product.
What is CBD?
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid, or chemical compound, found in cannabis. Cannabidiol is the second-most abundant cannabinoid in the plant after tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). It has many potential therapeutic benefits, including anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-anxiety, and seizure-suppressant properties. CBD is sourced from both cannabis and hemp plants.
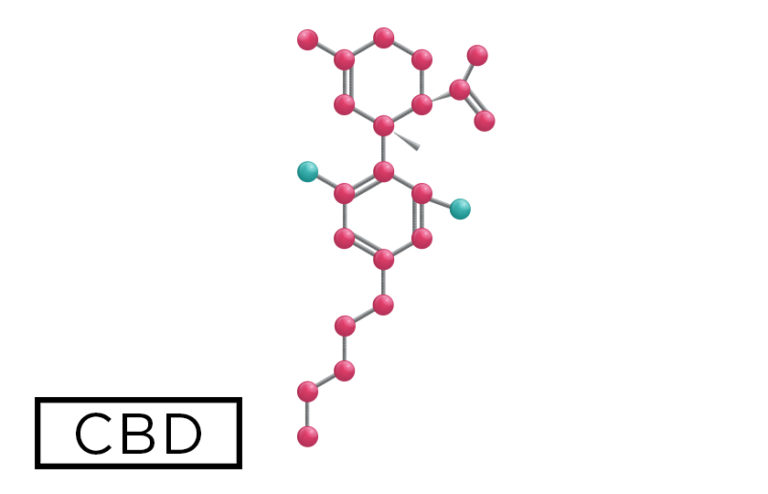 Photo by: Weedmaps
Photo by: WeedmapsImage lightbox

You can find three main types of CBD products online and in dispensaries:
- Full-spectrum: CBD that contains all the naturally occurring compounds found in the cannabis or hemp plant it's sourced from. The final product of full-spectrum CBD also includes trace amounts of THC, other cannabinoids like CBG and CBN, and terpenes. By containing the full suite of chemicals in the plant, full-spectrum CBD products are more likely to produce the "entourage effect," in which the compounds work together to enhance potential therapeutic benefits. They may also produce mildly psychoactive effects due to the trace amounts of THC, usually less than 0.3%.
- Broad-spectrum: Manufacturers of broad-spectrum CBD products reduce the THC content to non-detectable levels, typically less than 0.01%. However, it still contains a wide range of cannabinoids, terpenes, and other potentially beneficial compounds in the source cannabis plant.
- Isolate: CBD isolate is the purest form of CBD. These products only contain CBD and no other cannabis compounds. Several rounds of processing result in a crystalline, white powder that is 99%+ pure CBD.
The history of CBD
Like many cannabinoids, the origin story of CBD's popularity began in a lab. In 1940, the Harvard-trained organic chemist Roger Adams successfully extracted CBD from cannabis for the first time. By 1963, Dr. Raphael Mechoulam, known as the “godfather of cannabis research,” took the baton from Adams and described the chemical structure of CBD. This advancement helped create a foundation for understanding not only CBD, but THC as well. Mechoulam's discovery of CBD's chemical structure contributed to demystifying THC's chemical structure in 1964. His research linked psychoactive and euphoric effects to THC and dissociated CBD as an intoxicating compound.
 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

As a result, CBD remained overshadowed by its intoxicating counterpart throughout the mid-20th century as researchers predominantly focused on THC's psychoactive effects. It wasn't until the late 20th and early 21st centuries that scientists began actively exploring the potential therapeutic benefits of CBD, leading to a resurgence of interest in this non-intoxicating cannabinoid. Today, CBD is at the forefront of many studies, clinical trials, and discussions surrounding its applications for various health conditions and wellness purposes.
How is CBD made?
CBD is extracted from either cultivated hemp or low-THC cannabis strains.
- Cannabis-derived: Cannabis-derived CBD is extracted from cannabis plants that are generally grown and consumed for their intoxicating properties. US law defines intoxicating cannabis plants as containing more than 0.3% THC. While THC is the predominant cannabinoid in most weed plants, several strains are richer in CBD than THC, such as AC/DC and Cannatonic.
- Hemp-derived: Hemp-derived oil and CBD products are sourced from industrial hemp plants grown primarily for their fiber and seeds. These plants tend to differ from cannabis plants in appearance; they are often skinny and have sparse foliage. Hemp is also differentiated from cannabis by its low levels of THC. The 2018 Farm Bill outlines that a hemp plant must contain no more than 0.3% THC.
After harvesting the plant's flowers and leaves, extractors separate the CBD from the plant using methods like CO2 extraction, solventless extraction, or oil infusion. CBD undergoes refinement processes following extraction to isolate it from other compounds and remove impurities. Extractors then add the purified CBD back to products from oils and capsules to creams and edibles.
CBD vs. THC: What's the difference?
CBD and THC are two of the most well-known and studied cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, but have several key differences:
- Effects: THC is intoxicating, meaning it's responsible for the high or euphoric sensation weed produces. It binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, altering perception, mood, and consciousness. CBD is non-intoxicating, meaning it does not produce a high. It does not bind strongly to the same receptors as THC, so it doesn't produce the same psychoactive effects.
- Legality: THC is classified as a controlled substance in the US. It's legal for medical and/or recreational use only in the regions where cannabis use is legal. CBD derived from hemp plants with less than 0.3% THC is legal in all 50 states, while CBD derived from cannabis remains subject to local legal restrictions.
- Potential therapeutic benefits: THC has been used for its purported analgesic (pain-relieving), anti-nausea, and appetite-stimulating properties. It's prescribed in some medical treatments, particularly for chronic pain, chemotherapy-induced nausea, and muscle spasms in conditions like multiple sclerosis. CBD has gained attention for having potential therapeutic properties without causing intoxication. It's being explored for its anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, antipsychotic, and anticonvulsant properties. It's commonly used in products for conditions like anxiety, epilepsy, and chronic pain.
- Potential side effects: As mentioned, THC has intoxicating properties, which can cause side effects such as impaired coordination, memory and cognitive issues, and increased heart rate. It may also lead to anxiety or paranoia in some individuals, especially at high doses. CBD is generally considered well-tolerated and has a low risk of side effects. Some consumers have reported mild side effects like drowsiness, dry mouth, and changes in appetite.
How to consume CBD
There are several ways to consume CBD. Consider these common methods:
- Oral: CBD oils, edibles, drinks, and tinctures are some of the most popular and versatile ways to consume CBD. For fast, sublingual absorption, you can place a few drops of CBD oil or tincture under your tongue and hold it there for 30 - 60 seconds before swallowing. Capsules, soft gels, edibles, and drinks provide a convenient and precise way to take CBD. They offer consistent dosing but may take longer to go into effect compared to sublingual methods.
- Inhalation: Vaping CBD involves inhaling vaporized CBD liquids using a vape pen or tabletop vaporizer. Vaping provides a quick onset of effects but may not be suitable for everyone due to potential lung health concerns associated with vaping. The same concern applies to smoking high-CBD strains via pipe, bong, or joint.
- Topical: CBD creams, balms, and lotions are designed for potential localized relief of pain, inflammation, and skin issues. They do not enter the bloodstream and are primarily used for surface-level relief.
How to dose CBD
While further research is required to pinpoint the optimal CBD dosage for each individual, existing studies can help narrow down the best dosages for certain ailments and medical conditions. For instance, Mayo Clinic, the US-based nonprofit academic medical center, released a review that can be used as a starting point for THC and CBD dosage measurements.
 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

Based on information in the review, starting with a dose of 2.5 - 10 milligrams of CBD may be helpful to reduce anxiety, or 160 milligrams for inflammation. If you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking other medications, consult a healthcare professional before consumption.
How long do CBD's effects last?
The duration of CBD's effects can vary widely from person to person, depending on several factors. Here's a general overview of how long the effects of CBD may last for different methods of consumption:
- Oral: When you consume CBD orally via edibles, drinks, and tinctures, it usually takes around 30 minutes to two hours for any observable effects to kick in. After that, the effects of orally ingested CBD can last anywhere from 4 - 6 hours. However, depending on the dose, some individuals may experience prolonged effects lasting up to eight hours or more.
- Inhalation: Vaping or smoking CBD provides the quickest onset of effects, usually within a few minutes. However, the effects of inhaled CBD also tend to be shorter-lived, lasting around 1 - 3 hours.
- Topical: When applying CBD topically, your skin absorbs the CBD, which means it may take some time to penetrate and interact with the endocannabinoid receptors in the skin. The effects of topical CBD (like potential pain relief) are generally localized and may last several hours. However, they do not typically enter the bloodstream, so the duration can vary depending on factors like skin type and the specific product.
Is CBD legal?
In the US, hemp-derived CBD products with less than 0.3% THC are legal at the federal level, thanks to the 2018 Farm Bill. This bill removed hemp from the US's list of controlled substances.
 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

That said, individual state laws regarding CBD vary widely. Some states have stricter regulations on where you can buy CBD products and how you can use them, while others are more lax. Cannabis-derived CBD is subject to state-specific medical and recreational cannabis laws. Check your local laws before purchasing CBD products.
What is CBD used for?
Research into CBD has been conducted for the following conditions:
- Pain relief and anti-inflammation: According to research in the National Library of Medicine, when CBD is introduced to our endocannabinoid system, it prevents the body from absorbing a pain-regulating compound known as anandamide, an endogenous cannabinoid. Inhibiting the absorption of this compound shunts excess quantities into the bloodstream, which in turn may reduce pain. CBD may also target specific spinal receptors, helping to suppress pain and inflammation. In both human and animal models, CBD seems to have a variety of anti-inflammatory properties.
- Epilepsy and seizures: CBD has been documented as a potential antiepileptic since 1881 and was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating severe types of childhood epilepsy in 2018. However, its anticonvulsant mechanisms still need to be fully understood. One possible explanation for CBD's perceived neuroprotective effects is its interaction with NMDA receptors, which play a crucial role in the type of neuronal activity that's a hallmark of epilepsy.
- Addiction treatment: In 2015, researchers from the University of Montreal conducted a comprehensive review of CBD as an intervention for addictive behaviors. They concluded that CBD might have a beneficial impact on opioid, cocaine, and psychostimulant addiction. In addition, studies suggest that CBD may also help treat tobacco addiction. One reason may be CBD's potential ability to ease the anxiety that leads people to crave drugs such as heroin.
Consumers report using CBD for various health and wellness reasons, but more research is needed to determine the conditions it can most successfully treat.
What are the side effects of CBD?
While generally considered safe and well-tolerated for most people, CBD has a few reported side effects that can appear when consumed in high doses:
- Dry mouth: CBD may reduce saliva production, leading to a dry sensation. Drinking water or staying hydrated can help alleviate this side effect.
- Dizziness: Some people experience dizziness or lightheadedness when taking high doses of CBD. Start with the lowest dose possible and gradually increase it to avoid this effect.
- Changes in appetite: You may experience increased or decreased hunger due to taking CBD.
- Diarrhea: Extremely high doses of CBD (hundreds of milligrams) may cause gastrointestinal issues, including diarrhea.
- Drowsiness: You may experience drowsiness or tiredness when taking high doses of CBD, especially if you use CBD with other sedating products like melatonin. This side effect may be beneficial if you want to improve your sleep.
- Medication interactions: CBD may interact with certain medications that are metabolized by the liver. Consult with a healthcare professional before taking CBD with other medications.
- Blood pressure: CBD may cause temporary changes in blood pressure, including a slight drop in blood pressure for some people.
Responses to CBD vary widely depending on the dose, person, and medical history. Pay attention to how your body reacts to CBD and adjust your dosage or consumption method as needed. Seek medical advice from your doctor when starting a CBD regimen for the first time.
Where can you buy CBD products?
Here are the most common places where you can buy CBD products, ranked from best to worst:
- Dispensaries: In regions where medical and/or recreational cannabis is legal, you can find reputable CBD products at licensed cannabis dispensaries. These dispensaries typically offer a range of CBD options, including oils, tinctures, edibles, and more. At dispensaries, you can find lab-tested CBD products that contain varying levels of CBD isolate, full-spectrum CBD, and various THC:CBD ratios.
- Pharmacies: Some pharmacies and drugstores offer CBD products over the counter. You can typically find a limited selection of CBD oils, creams, and capsules at pharmacies with detailed product labels.
- Health stores: Many health food and wellness shops now carry CBD products, including oils, capsules, topicals, and other wellness products. Read the labels to determine whether these products contain the right dosage for your body.
- Brick-and-mortar specialty stores: While dedicated CBD shops have a wide (sometimes overwhelming) selection of products, it may take some research on your part to vet the brands and products offered.
- E-commerce stores: Online retailers offer convenience and access to a huge range of products, but it'll require a lot of research to determine which retailers are reputable. Look for websites that provide third-party lab testing, customer reviews, and detailed product information. Some brands that sell cannabis-derived CBD products in dispensaries also sell hemp-derived CBD products online. These retailers are some of the best to consider.
- Gas stations: Plenty of gas stations provide CBD-infused capsules, elixirs, and drinks, but it's essential to exercise caution when perusing these products as they may not contain any actual CBD. A November 2017 study showed that of 84 CBD products from 31 companies, only 30.95% were accurately labeled with the correct amount of CBD.
What to look for in CBD products
While sifting through the vast ocean of CBD products available online and in stores, it's important to know what to look for to find the best possible products:
- Certificate of analysis: It's imperative to find CBD oil or CBD-infused products from a reputable source — preferably one that includes a certificate of analysis from a third-party testing lab. The amount of CBD inside the product and other potential ingredients can be confirmed by third-party product verification without solely relying on the manufacturer's word.
- Detailed product label: Aside from proof of third-party testing, reputable CBD products provide additional information. Look for the amount of active CBD per serving, a supplement fact panel that lists other ingredients, net weight, manufacturer or distributor name, suggested use, type of CBD (full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, or isolate), batch and date code, and expiration date.
- THC:CBD ratio: Know whether the CBD product you're considering contains any THC and, if so, what the exact CBD-to-THC ratio is. For instance, a CBD oil that claims to offer a 3:1 CBD:THC ratio will have around three times more CBD than THC. The higher the amount of CBD, the more you'll be protected from the undesirable effects of THC, such as anxiety and paranoia.
Bottom line
We're just beginning to learn the many ways CBD and other cannabinoids work together to alter the way we feel. While CBD is relatively safe with few side effects, it's important to research before trying new products. If you have any medical conditions or are taking medications, speak with a healthcare professional before starting a CBD regimen.
FAQ
Can you overdose on CBD?
CBD has an extremely low risk of overdose, and it has never been shown to be fatal. However, extremely high doses may lead to uncomfortable side effects such as dizziness, fatigue, or gastrointestinal discomfort.
Following dosing guidelines and starting with a low dose of 10 milligrams or less is important.
Is CBD safe?
Generally, yes. CBD is considered safe for most people when a reputable product is used as directed. However, your response may vary depending on the dose and product. Some people experience mild side effects like dry mouth, dizziness, or changes in appetite. It's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before using CBD, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking other medications.
Can CBD contain THC?
That depends. Legally, CBD products derived from hemp should only contain trace amounts of THC (typically less than 0.3%). However, CBD products with higher THC concentrations can be found at dispensaries in regions where cannabis is legal. Check product labels and third-party lab reports to verify the THC content of any product.
Does CBD show up on a drug test?
In most cases, it's highly unlikely that CBD will show up on a drug test. Typically, employment drug tests look for the presence of THC or THC metabolites. Most employers abide by the guidelines set forth by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services (SAMHSA), which includes detection for THC but not CBD. Tests generally look for THC, but how much and how long THC sticks around depends on what's being tested.
How long is CBD detectable in urine?
It's unlikely that a urine test will be looking for CBD. Still, THC may be detected in urine for up to three days in occasional users, 5 to 7 days in moderate users, 10 to 15 days in daily users, and more than 30 days for chronic users who consume multiple times a day.
What is liposomal CBD?
Liposomal CBD improves the bioavailability of the cannabinoid by surrounding it with a substance that the body can more easily absorb. This novel format appears to increase CBD's bioavailability so its potential benefits can be more effectively delivered and distributed.
Is CBD water-soluble?
Not naturally. In water-soluble CBD formulations, the CBD molecules are manipulated to dissolve better in water. However, the term “water-soluble” is inaccurate since CBD molecules will never fully dissolve in water but can be transformed into a more water-compatible form.
Is CBD addictive?
No, CBD is not considered addictive. Because CBD doesn't produce the high associated with THC, scientists think it has limited potential for abuse. Some research suggests CBD could help as a treatment for addiction.
How much do CBD products typically cost?
The price of CBD products varies dramatically depending on the product type, brand reputation, CBD concentration, extraction method, and more. For example, licensed, lab-tested CBD oils typically cost at least $50 to $60 per 1,000-milligram bottle, which comes out to a total cost of five cents per milligram of CBD or more.
Does CBD expire?
Yes, CBD products expire. The shelf life depends on how you store the product, how it was packaged, and the product type. CBD oil has a shelf life ranging from 14 months to two years when stored in a cool, dark place.