Known since 1944, when American chemist Roger Adams first synthesized and subsequently patented it, HHC's commercial use and public consumption is a relatively new fad that comes on the heels of the semi-synthetic cannabinoid trend.
Learn more about this unique cannabinoid and its legality and efficacy.
What is HHC?
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid, meaning it's a hydrogenated derivative of Delta-8 THC or Delta-9 THC, two intoxicating cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. Hydrogenation is a process by which molecular hydrogen (H2) is added to another compound or element — in this case, Delta-8 or Delta-9 THC.
 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

HHC is most often synthesized from Delta-8 THC, which itself is most often synthesized from hemp-derived CBD. Once CBD is extracted from hemp plant material, it's refined into an isolate, synthesized into Delta-8 THC, and then further processed into HHC, typically using heavy metals such as platinum, palladium, or mercury.
HHC is reported to produce similar effects to THC but is generally considered to be less potent, although this can depend on the specific HHC isomer and individual body chemistry.
HHC vs THC: What's the difference?
HHC and THC are both cannabinoids, but they have distinct differences:
- Research: THC is one of the most researched cannabinoids with well-documented effects, benefits, and risks. HHC is less studied, and much of the information about it comes from anecdotal reports.
- Chemical structure: THC has a double bond in its molecular structure, which is crucial for its psychoactive effects. HHC is similar but has an added hydrogen molecule, altering its structure. This hydrogenation process makes HHC more stable and less susceptible to UV light and heat degradation.
- Effects: Both HHC and THC are psychoactive, but their effects can vary. THC is known for its potent psychoactive effects, including euphoria and altered sensory perception, while HHC is reportedly milder.
- Availability: THC is widely available in regions where it's legal, in various forms like flowers, edibles, concentrates, and tinctures. HHC, being newer and less regulated, is not as widely available but can be found in similar product forms, including gummies.
- Legality: THC, specifically Delta-9 THC, is federally illegal in many places, though some regions have legalized it for medical or recreational use. HHC, being a derivative of hemp and not directly from cannabis, often exists in a legal gray area. It's not explicitly legal or illegal under federal law in the US.
- Potency: THC is known for its ability to build tolerance in users over time. HHC may also build tolerance, but possibly at a different rate. The potency of HHC can vary based on the ratio of its active isomers (9R-HHC and 9S-HHC), with 9R-HHC being more potent.
How is HHC made?
HHC is made through a chemical process known as hydrogenation. This process involves modifying the structure of THC — typically derived from hemp — by adding hydrogen molecules.
 Photo by: Tony Brown/Weedmaps
Photo by: Tony Brown/WeedmapsImage lightbox

Here's a simplified overview of the process:
- Starting material: The process begins with THC, often derived from hemp, to comply with legal restrictions.
- Hydrogenation process: The THC is exposed to high pressure and a catalyst, typically a metal like palladium or nickel, in the presence of hydrogen gas. This process adds hydrogen atoms to the THC molecule.
- Chemical alteration: Adding hydrogen atoms changes THC's molecular structure, breaking down its double bonds. This results in the formation of HHC.
- Isomerization: The hydrogenation process results in a mixture of different HHC isomers. The most common isomers are 9R-HHC and 9S-HHC, which are stereoisomers of each other (mirror images). The ratio of these isomers can affect the potency and effects of the final product.
- Purification and testing: After hydrogenation, the product is typically purified to remove residual solvents or catalysts. It's then tested to determine the concentration of HHC and the presence of other compounds.
- Formulation into products: The purified HHC is formulated into various products, such as vape cartridges, edibles, and tinctures.
Does HHC get you high?
Yes, HHC has psychoactive effects, and it can get you high. HHC's effects will vary from person to person, but it's generally considered to be similar to THC, with effects ranging from sleepiness to relaxation and euphoria.
Does HHC have any side effects?
Little is known about the potential side effects of consuming HHC. However, we do know there are common side effects associated with THC and its derivatives that you may experience:
- Intoxication: Like THC, HHC can produce intoxicating effects, such as euphoria or altered perception — a benefit to many but a side effect to some as well.
- Physical discomfort: Dry mouth, red eyes, and increased heart rate are common side effects of THC and other derivatives.
- Cognitive impairment: THC affects memory, concentration, and decision-making, so it's likely HHC produces similar effects in high doses as well.
- Anxiety: When consumed in high doses, THC can cause anxiety or paranoia. HHC is likely to produce the same side effects in high doses.
- Impaired coordination: As with any intoxicating drug, impaired motor skills and coordination can occur. Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery after consuming THC or HHC.
Is HHC safe?
It depends. Making HHC is complex and, when done poorly, can lead to a soup of unidentified and potentially unsafe residual solvents, heavy metals, and other compounds. Additionally, many products labeled as “pure" HHC contain Delta-8 THC, Delta-9 THC, and other non-natural cannabinoids that are not included on the label.
 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

Consuming HHC is not recommended, as it's potentially dangerous, and we do not have enough studies or information about how it interacts with the human body.
Does HHC have any medical benefits?
Other than anecdotal evidence on pain relief and other effects similar to CBD, there is no scientific evidence that HHC has any medical benefits. In fact, there are no studies on HHC, so we don't really have any idea what it does.
Is HHC legal?
As a cannabinoid, HHC lives in a legal gray area, much in the same way that other synthesized cannabinoids like Delta-8 THC, Delta-10 THC, or THC-O do, and state approaches to these compounds vary widely. New York, for example, has included language in regulations that cover “synthetic cannabinoids" and “cannabimimetic agents" that may apply to compounds such as HHC. Other states, like Oregon, have banned all artificially-derived cannabinoids.
When synthesized from hemp-derived cannabinoids like CBD, some producers feel the compounds are legal since hemp and its derivatives are legal. However, since the hemp-CBD marketplace remains largely unregulated, these products can be produced with highly variable levels of quality and safety. Both state and federal positions on HHC may change, and regulations will become more refined, but research the current status of these substances before you purchase them.
What types of HHC products are there?
HHC products are available in all the ways that THC and CBD products are, including:
- Vape cartridges: The most popular HHC product, vape cartridges, contain HHC distillate, typically connected with a 510-thread vape battery.
- Edibles: HHC can be found in gummies, chocolates, and other infused foods. Edibles may offer a discreet and easy method of consumption, but they typically take longer to take effect compared to inhalation.
- Tinctures: HHC tinctures are liquid extracts that you can take orally or add to food and beverages.
- Capsules: The precise dose in each HHC capsule or pill makes dosing straightforward. Similarly to edibles, capsules can take up to two hours to take effect.
- Concentrates: You can find HHC in concentrated forms like shatter, wax, or crumble, which you dab.
- Topicals: Although less common, you may be able to find HHC in topical products like creams, balms, or salves. These are applied directly to the skin and are used for localized effects.
Where can you buy HHC products?
You can purchase HHC products from various sources, but availability largely depends on local laws and regulations.
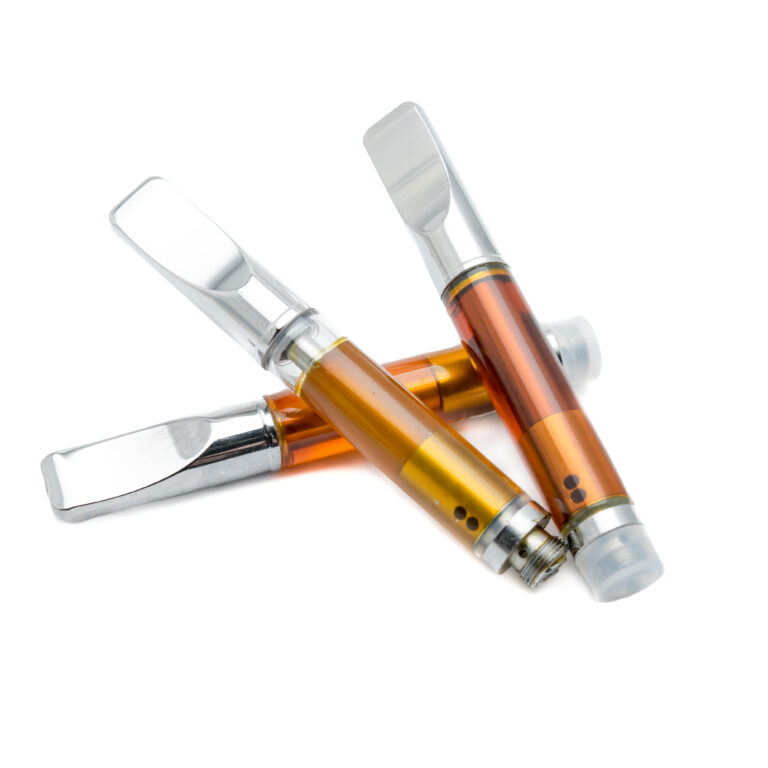 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

Here's where you might find HHC products:
- Dispensaries: In regions where cannabis is legal, dispensaries may carry a range of HHC products. These establishments often provide knowledgeable staff who can advise on product selection and dosage.
- Smoke/vape shops: Some smoke and vape shops have expanded their inventory to include HHC and other hemp-derived products. These shops are more common in areas with relaxed cannabis laws.
- Health and wellness stores: Some health and wellness stores, especially those specializing in natural or alternative remedies, may stock HHC products.
- Online retailers: Many online stores specialize in hemp and cannabis-related products, including HHC. This is often the most accessible option, especially for areas without physical retail outlets. However, verifying the legality of HHC in your jurisdiction is important before making a purchase.
Bottom line
HHC is one of a growing number of THC alternatives that have emerged after the legalization of hemp. The compound is made through a hydrogenation process that typically starts with hemp-derived THC and reportedly produces effects that are comparable to THC. However, there are real concerns about potential heavy metal contamination and exposure to other unknown substances that are produced during the manufacturing process. Most experts do not recommend using HHC until it is regulated and studied.
We need more research examining the effects and potential benefits of HHC, and consumers should ensure that any HHC products they purchase have been tested for purity and safety by an independent third-party laboratory.
FAQ
How long does it take HHC to kick in?
The onset time for feeling the effects of HHC varies greatly depending on the method of consumption. When inhaled, you can feel the effects almost immediately, typically within minutes. When ingested, the onset can take 30 minutes to two hours. Consuming tinctures sublingually (under the tongue) can lead to effects being felt within 15 to 45 minutes. If applied topically, HHC might not produce the intoxicating effects typically associated with inhalation or oral consumption since it's used for localized effects on the body.
HHC vs. delta-8 THC: what's the difference?
While HHC and delta-8 share similarities, there are some key differences:
- Chemical makeup: HHC and delta-8 THC have similar molecular structures, though there's a missing double bond in HHC's structure.
- Effects: Both cannabinoids reportedly offer effects like euphoria and pain relief but with varying potency. Delta-8 is known for being less intense than delta-9 THC. HHC, existing in two forms (9R-HHC and 9S-HHC), shows differing potencies, with 9R-HHC often reported as more potent. Consumer experiences with HHC vary; some find it less potent than delta-8, and others more so.
- Popularity: Delta-8 THC is more established in the consumer market compared to the newer HHC. However, many companies offering delta-8 THC now provide HHC products.
- Products and price: HHC and delta-8 THC are available in various forms, including vapes, gummies, and tinctures. Prices are generally similar and lower than delta-9 THC products.
HHC vs. delta-10 THC: what's the difference?
Just like delta-8 THC, HHC and delta-10 THC differ. HHC is a hydrogenated form of THC and is known for its stability and resistance to heat and UV exposure, potentially offering a longer shelf life. It's often described as providing a moderate high, with effects that are somewhat between delta-8 and delta-9 THC. Delta-10 THC, on the other hand, is a minor cannabinoid, but it's less potent than delta-9 THC.
Both HHC and delta-10 THC are synthesized through chemical processes, and their legal status can vary depending on local laws — especially considering their relation to THC, the main intoxicating compound in cannabis.
How long does an HHC high last?
The duration of an HHC high varies widely based on several factors, including the method of consumption, your metabolism, tolerance, and the dosage taken. Generally, the effects can last anywhere from 2 - 3 hours when inhaled. Consumed orally, the effects can last much longer, typically ranging from 4 - 8 hours.
Will HHC show up on a drug test?
The short answer: it might. Without human studies looking at how HHC is broken down and metabolized in the body, we don't know if it could cause someone to fail a drug test. Anecdotal reports suggest it might not, but there's some animal evidence to suggest that HHC produces similar metabolites as THC. Additionally, there have been reports that some HHC products contain delta-9 THC, which is what most standard drug tests are screening for.
This article was reviewed by Bonni Goldstein, MD, a physician specializing in cannabis medicine in Los Angeles, California, owner and medical director of CannaCenters, and medical advisor to Weedmaps.com.




