Cannabinoids are a group of chemical compounds that both cannabis plants and the human body produce. Learn how the three types of cannabinoids interact with our bodies and what major and minor ones you should know.
Types of cannabinoids
There are three types of cannabinoids:
- Phytocannabinoids: "Phyto" means "plant" in Greek — phytocannabinoids are chemicals that occur naturally in cannabis plants. Over 140 different phytocannabinoids have been identified, with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) being the most well-known. Phytocannabinoids interact with the human body's endocannabinoid system (ECS) and non-cannabinoid receptors, influencing various physiological processes.
- Endocannabinoids: "Endo" is short for "endogenous," meaning originating within the body. Endocannabinoids are internally produced cannabinoids and essential to our bodies' ECS. As part of the human ECS, endocannabinoids help regulate bodily functions such as appetite, pain, mood, and memory. Anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) are two of the most studied endocannabinoids.
- Synthetic cannabinoids: Synthetic cannabinoids are artificially manufactured chemicals designed to mimic the effects of natural cannabinoids found in cannabis. THC-O, HHC, and THC-H are synthetic cannabinoids chemically related to THC. These synthetic versions can be much more potent and unpredictable than phytocannabinoids. They bind to the same cannabinoid receptors in the brain as THC, but their chemical structure is different from the naturally occurring cannabinoids in cannabis. You will often find synthetic cannabinoids in products marketed as "synthetic marijuana" or "legal highs" under names like Spice or K2. However, these products can have dangerous side effects like a rapid heart rate, vomiting, and hallucinations.
What are acidic cannabinoids?
Acidic cannabinoids are the original forms, or the precursors, of cannabinoids found in fresh, unprocessed cannabis buds. These compounds have a carboxylic acid group attached to them, which makes them different in structure and function from their more commonly known "activated" counterparts.
 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

Well-known acidic cannabinoids are THCA, CBDA, and CBGA. When you heat or age flower, a process known as decarboxylation occurs and converts these acidic cannabinoids into their commonly recognized forms: THC, CBD, CBG, etc.
Benefits of acidic cannabinoids
You can consume acidic cannabinoids via tinctures and other products designed to be consumed rather than smoked. They're not as lipophilic (easily dissolved in fat as opposed to water) as decarboxylated cannabinoids and, therefore, are absorbed easier by the body, allowing for lower dosing when compared to THC and CBD.
While research into acidic cannabinoids is still emerging, several potential benefits have been identified:
- Anti-inflammation: THCA, CBDA, and CBG have shown promise in helping to reduce inflammation. This could benefit conditions like arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and neuroinflammation.
- Neuroprotection: Studies suggest that acidic cannabinoids, particularly THCA, might have neuroprotective properties. This could be important for diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
- Anti-nausea: CBDA has been found in some studies to be a potent anti-nausea and anti-vomiting agent, potentially more so than CBD. This could be helpful for individuals undergoing chemotherapy or other treatments known to cause nausea.
- Pain relief: While less potent than their decarboxylated counterparts, acidic cannabinoids like CBDA may offer pain relief, particularly in conditions like muscle pain and neuropathic pain.
- Non-intoxicating: THCA is mostly non-intoxicating, meaning it does not produce the high associated with cannabis. This makes it appealing to patients who want the therapeutic benefits without the intoxication. However, THCA products still contain a small amount of THC, so there is a slight risk of intoxication depending on the person using the product and how much THC is present.
It's recommended that THCA, CBDA, and CBGA products be stored in the refrigerator to prevent decarboxylation, which can occur over time at room temperature.
What are activated cannabinoids?
Activated cannabinoids, also known as decarboxylated cannabinoids, result from acidic cannabinoids shifting into their active forms. This transformation typically occurs through decarboxylation — the application of heat.
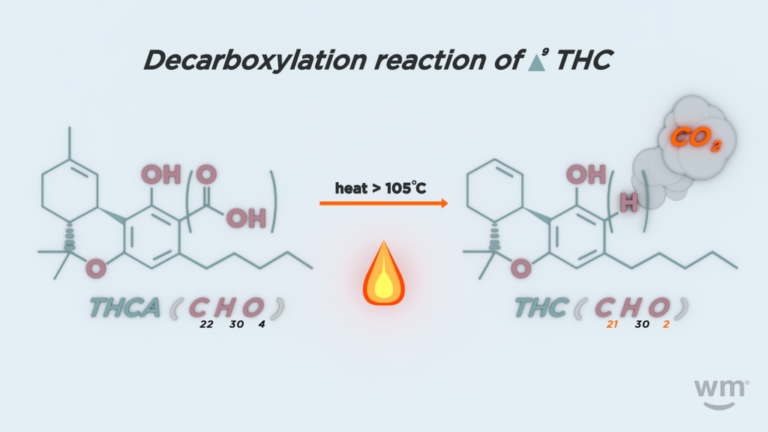 Photo by: Weedmaps
Photo by: WeedmapsImage lightbox

When cannabis is heated by smoking, vaporizing, or cooking, the heat removes the carboxyl group (COOH) from the THCA and CBDA molecules, converting them into THC and CBD.
Benefits of activated cannabinoids
For decades, researchers have been studying cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant and their effect on the mind and body. While research is ongoing, several key benefits have been observed so far:
- Anti-inflammation: THC and CBD have anti-inflammatory effects, which can be beneficial in alleviating conditions like arthritis and Crohn's disease.
- Pain relief: Cannabinoids — particularly CBD — have been found to help relieve chronic pain by altering pain perception pathways in the brain. This makes them a potential alternative to addictive drugs like opioids.
- Neuroprotection: Some studies suggest that cannabinoids may protect brain cells. CBD has been shown to help with epilepsy and may have the potential to treat neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease.
- Anxiety and depression management: CBD and low doses of THC have been found to have calming effects that can help reduce anxiety. Some people use it to alleviate symptoms of depression, though this area requires more research.
- Sleep: A side effect to some and a huge benefit to others, the drowsiness caused by sufficient doses of cannabinoids like CBD, THC, and CBN can help people dealing with insomnia.
- Cancer symptom relief: Cannabinoids like THC and CBD have been used to alleviate cancer-related symptoms and the side effects of cancer treatment, such as nausea, vomiting, and pain.
- Appetite stimulation: THC is known to increase appetite, which can be beneficial for individuals experiencing weight loss due to certain medical conditions or treatments.
- Addiction treatment: Cannabinoids may help treat substance use disorders by reducing withdrawal symptoms and dependency.
What do cannabinoids do in the body?
Cannabinoids interact with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex cell-signaling system identified in the late 1980s by researchers exploring THC, which was a well-known cannabinoid by then. The ECS consists of three core components:
- Endocannabinoids
- Receptors in the nervous system and around the body that endocannabinoids and cannabinoids bond with
- Enzymes that help break down endocannabinoids and cannabinoids
The two main cannabinoid receptors are CB1 receptors, mostly found in the central nervous system, and CB2 receptors, mostly found in your peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells. When cannabinoids enter the body, they interact with these receptors, influencing the ECS and thus affecting various bodily functions.
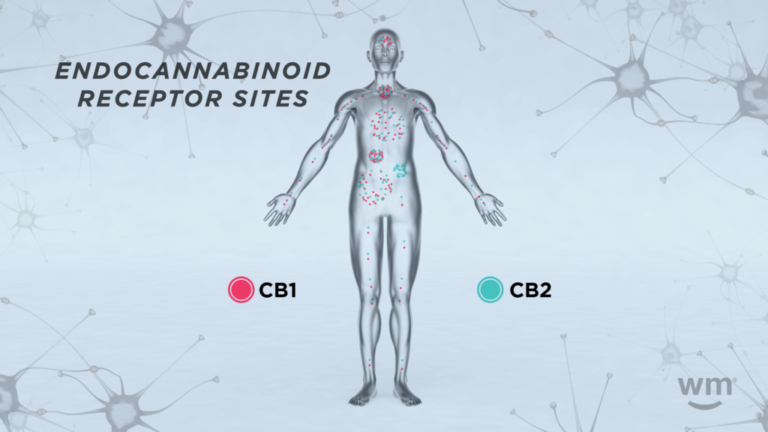 Photo by: Weedmaps
Photo by: WeedmapsImage lightbox

The exact effects depend on the type of cannabinoid consumed and the location of the receptors they interact with. For example, THC binds with CB1 receptors in the brain and can produce intoxicating effects; CBD does not bind as directly with CB1 or CB2 receptors and is non-intoxicating, instead influencing the body in more subtle ways.
List of major cannabinoids
You can find major cannabinoids in larger quantities in cannabis plants — at least 1% or more, depending on the strain. Each major cannabinoid found in the plant has unique properties and potential effects:
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): THC is the most well-known cannabinoid due to its intoxicating properties or the "high" it produces. People consume it for various medical purposes, including pain relief, appetite stimulation, and nausea reduction.
- Cannabidiol (CBD): CBD is a non-intoxicating compound known for its role in alleviating conditions like anxiety, epilepsy, inflammation, and pain.
- Cannabinol (CBN): Known for its mildly intoxicating effects, CBN is a degraded form of THC often found in aged cannabis. It's being researched for its potential sedative properties and as a possible treatment for insomnia and pain relief.
- Cannabigerol (CBG): A non-intoxicating cannabinoid similar to CBD, CBG was typically present in lower concentrations in most cannabis strains, but high-CBG strains have been developed in recent years. It's being studied for potential medical applications, including as an anti-inflammatory, neuroprotectant, and antibacterial agent. Its acidic precursor is CBGA.
List of minor cannabinoids
Minor cannabinoids typically appear in trace amounts in cannabis plants. Still, research progresses constantly, and they're worth learning about for their potential benefits:
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV): THCV is similar to THC but with slightly different effects and much less natural abundance in the plant. THCV is less intoxicating and is being researched for potential roles in weight loss and diabetes management.
- Cannabichromene (CBC): Another non-intoxicating compound similar to CBD, CBC has shown potential in contributing to the analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties of cannabis.
- Cannabidivarin (CBDV): Similar to CBD, CBDV is non-intoxicating and is being explored for its potential in treating epilepsy, autism, and other neurological conditions.
- Delta-8-THC: Delta-8 THC has intoxicating effects, although not as potent as delta-9-THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol), and is being investigated for potential anti-nausea and appetite-stimulating properties.
- Cannabicyclol (CBL): CBL is a rare, non-intoxicating cannabinoid. Cannabicyclolic acid (CBLA), its non-intoxicating precursor, has been studied for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Bottom line
Cannabinoids are key components of cannabis with significant potential for medical applications. Researchers are continually unlocking new possibilities in cannabis-centered healthcare and wellness. The benefits of cannabinoids range from pain and anxiety relief to potential neuroprotective properties and cancer-fighting abilities. As our scientific understanding grows, so does the opportunity for innovative treatments and applications.
FAQ
How many cannabinoids are there?
Chemists have identified over 140 different cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. As researchers develop more sophisticated techniques to study it, this number continues to grow. In addition to cannabinoids, cannabis plants contain terpenes and flavonoids, which also contribute to the overall strain's effects, characteristics, and therapeutic benefits.
What cannabinoids get you high?
THC is the primary cannabinoid known for its intoxicating effects. When consumed in sufficient doses, it binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, altering neural signals and leading to the “high” that people experience. Many consumers report feeling euphoria, altered time perception, relaxation, and increased appetite after consuming THC.
Is THC a cannabinoid?
Yes, THC is a cannabinoid and the main intoxicating component of cannabis. THC intoxication has been shown to increase blood flow to the prefrontal cortex, the brain region responsible for decision-making, attention, motor skills, and other executive functions. The exact nature of THC's effects on these functions varies from person to person. When THC binds to CB1 receptors, it can trigger feelings of euphoria in the brain's reward system.
Is CBD a cannabinoid?
Yes, CBD is the second-most-abundant cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. Though non-intoxicating, CBD can have psychoactive effects in the sense that it may be able to help with anxiety, chronic pain, and seizures.
This article was reviewed by Bonni Goldstein, MD, a physician specializing in cannabis medicine in Los Angeles, California, owner and medical director of CannaCenters, and medical advisor to Weedmaps.com.




