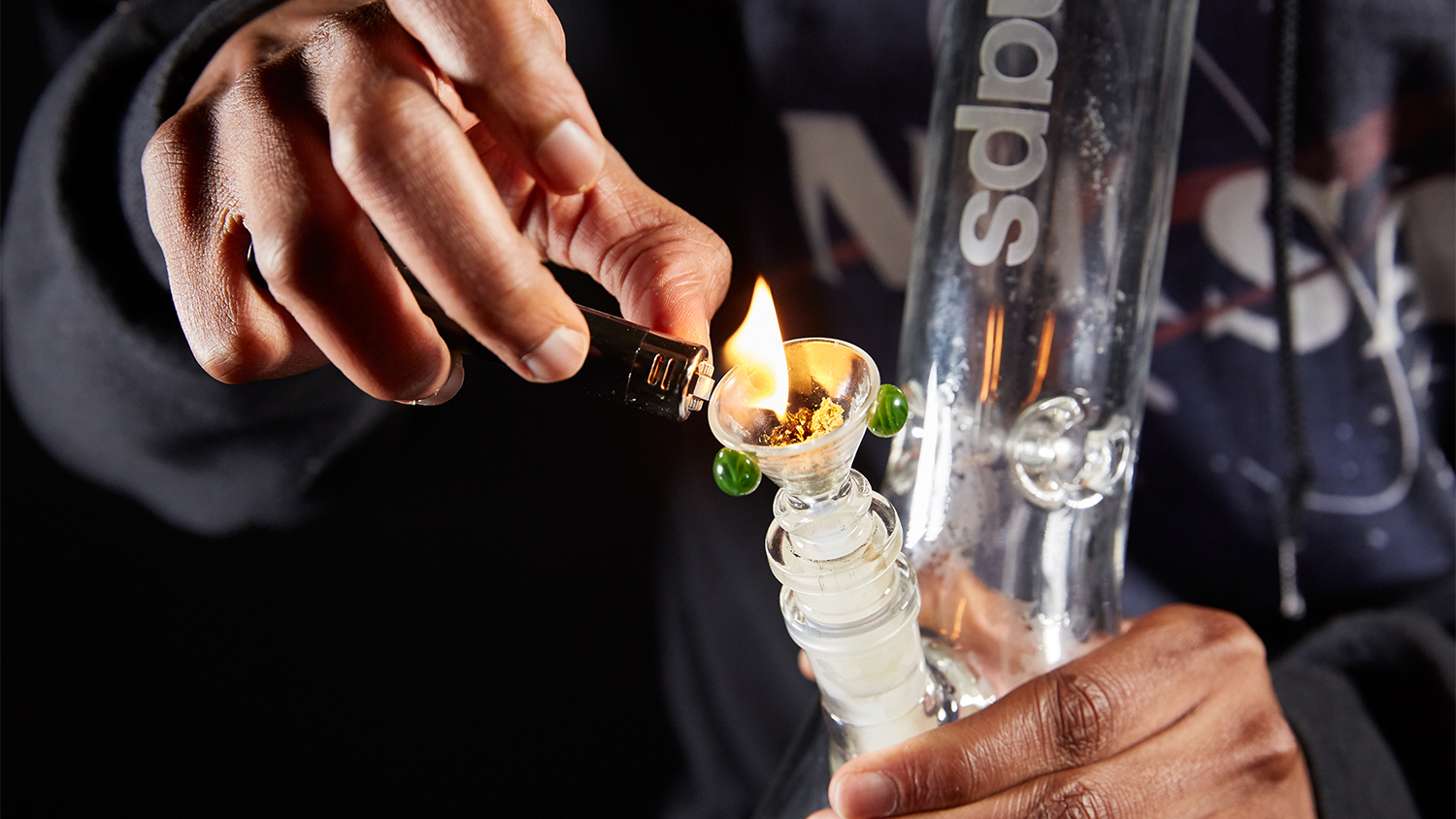
If you've ever wondered why eating raw cannabis doesn't produce a high, the answer lies in chemistry. The cannabis plant naturally produces THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) — a compound with potential health benefits but no psychoactive properties. It takes heat, light, or time to remove THCA's carboxyl group, transforming it into THC (delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol) — the psychoactive compound responsible for cannabis's classic euphoric effect. This process is called decarboxylation, and it's what turns potential into potency.
 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

What is THCA?
THCA is the acidic, non-intoxicating form of THC found in fresh cannabis. It's part of the plant's natural chemical composition before any heat is applied. The difference between THCA and THC lies in that extra carboxyl group, which keeps THCA from binding to the brain's cannabinoid receptors.
In the cannabis plant, THCA plays a protective role, helping defend against pests and environmental stress. For humans, its potential therapeutic benefits include pain relief, neuroprotective effects, and anti-inflammatory actions, although research is still in its early stages.
How THCA differs from THC
While THC delivers psychoactive properties and intoxicating effects, THCA does not. It exists in raw flower and freshly harvested cannabis plant material. Once heated — through smoking, vaping, or baking — THCA loses that molecular weight and becomes THC. The conversion is what enables cannabis products to produce mind-altering effects.
When you apply heat or allow time to pass, THCA's carboxyl group detaches — a chemical transformation known as decarboxylation. This process changes the molecule's chemical structure, allowing it to interact with the body's endocannabinoid system and produce psychoactive effects.
Potential health benefits of consuming THCA
Raw, un-decarboxylated cannabis may offer potential health benefits without psychoactivity. Early studies suggest it could support mental health, help manage inflammation, and provide nutritional cannabinoids that support balance in the body.
Research indicates that THCA may carry therapeutic benefits, including neuroprotective effects for conditions such as Alzheimer's, potential pain relief, and appetite stimulation; however, more human studies are needed.
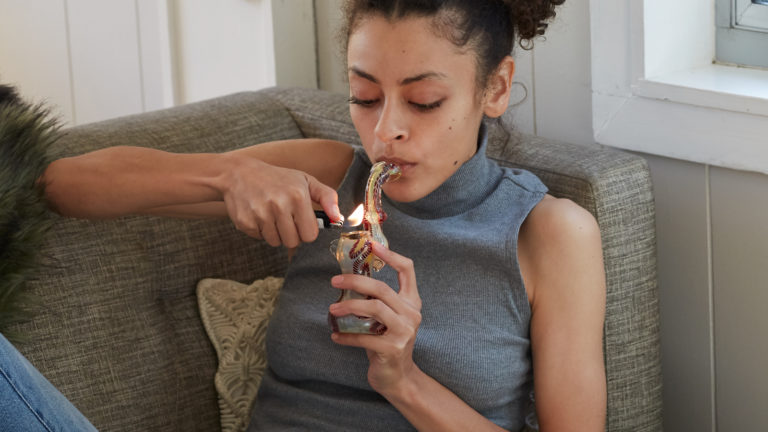 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

Why does THC get us elevated, and THCA doesn't?
The answer comes down to biology and molecular fit. THCA can't attach to CB1 receptors, which are the key docking sites in the brain responsible for producing a cannabis high. These receptors are concentrated in areas that control mood, perception, and coordination.
Because of its carboxyl group, THCA is too large to bind to CB1 receptors effectively. Without that connection, there's no psychoactivity — just subtle, non-intoxicating effects.
The role of CB1 receptors
CB1 receptors are located throughout the brain and central nervous system. When THC interacts with them, it triggers the psychoactive properties that lead to euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception. THCA, on the other hand, bypasses these sites entirely.
So which cannabinoids cause intoxication?
THC and THCV are known for their psychoactive properties. Other cannabinoids like CBD, CBDA, and THCA influence mood and physiology differently but lack the same mind-altering effects.
 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

How THCA becomes THC
Inside your pipe, oven, or vaporizer, science happens fast. When THCA is heated, it undergoes decarboxylation, shedding its carboxyl group and converting into delta-9 THC.
Decarboxylation is essential for activating THC's psychoactive compound potential. Your body doesn't decarb THCA efficiently on its own. That's why eating raw cannabis doesn't cause a high — it passes through your digestive system mostly unchanged.
Without heat, THCA remains dormant, unable to cause the intoxicating effects or therapeutic benefits associated with THC.
The decarboxylation process
The decarboxylation process determines whether cannabis stays mellow or turns mind-bending. Here's how it happens through different consumption methods:
- Sunlight conversion: Over time, UV exposure slowly activates THCA.
- Room-temperature conversion: Even at 77°F (25°C), THCA converts naturally, though gradually.
- Smoking: Intense, fast heat transforms THCA immediately but burns off some terpenes.
- Vaporizing and vape pens: Controlled heat keeps terpenes intact and minimizes side effects like dry mouth.
- Dabbing: High temperature equals full activation and strong potency.
- Baking: Ideal for edibles and gummies, balancing flavor and full decarb activation.
THCA isn't the only cannabinoid acid
When cannabis is freshly harvested, it's rich in acidic cannabinoids like THCA, CBDA, and CBGA — precursors to their better-known forms. These compounds exist before exposure to heat.
At harvest, the plant's chemical composition contains these acids in abundance. Once heated or aged, they convert into the active forms (THC, CBD, and CBG) found in most cannabis products.
Potential benefits of other cannabinoid acids
- CBDA: May offer anti-anxiety and anti-nausea support.
- CBGA: Sometimes called the “mother cannabinoid,” it's the starting point for many others.
- THCVA: Studied for potential metabolic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Decarboxylation activates these cannabinoids, allowing them to interact with cannabinoid receptors and deliver their therapeutic effects through the body's endocannabinoid system.
Bottom line
THCA and THC tell the story of potential and payoff. THCA is the promise — raw, stable, and full of possibility. THC is the product of transformation, delivering the psychoactive properties and therapeutic benefits that define cannabis use. Understanding their key differences helps consumers, patients, and enthusiasts make informed decisions about cannabis products, consumption methods, and desired effects of THC.
Once the spark of heat hits, THCA becomes THC — and the cannabis plant reveals its full spectrum of power.
Order weed for pickup or delivery from a dispensary near you.
FAQ
What are the benefits of THCA?
THCA may offer potential health benefits, including pain relief, anti-inflammatory effects, appetite stimulation, and neuroprotective effects, which could help protect the brain from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's. It delivers these therapeutic effects without causing a high.
Is THCA illegal?
THCA's legal status varies by location. Under the Farm Bill, hemp-derived products containing less than 0.3% delta-9 THC are federally legal. However, once heated, THCA becomes THC, which can reclassify it as a controlled substance under specific state laws. Always check local regulations and licensed dispensaries for clarity.
Will THCA make me fail a drug test?
Yes. Because THCA converts into THC during cannabis use or storage, it can produce THC metabolites detectable in the body. Even consuming raw products carries some risk of a positive result.
What is the difference between CBD and THCA?
CBD and THCA are both non-intoxicating, but they differ in their molecular structures and effects. CBD interacts indirectly with cannabinoid receptors, while THCA can't bind effectively until it is heated into THC. CBD is known for therapeutic benefits like anxiety relief and inflammation control; THCA's potential lies in its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties.
Major contributions from Dr. Adie Rae.