The most common cannabinoid found in the raw cannabis plant. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, or THCA, is non-intoxicating but converts into intoxicating THC when exposed to heat through a process called decarboxylation. Research indicates that THCA has its own medicinal potential in anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-emetic treatments.
What's the difference between THC and THCA?
You won't get high from eating a raw cannabis plant because the THCA has not yet converted to THC.
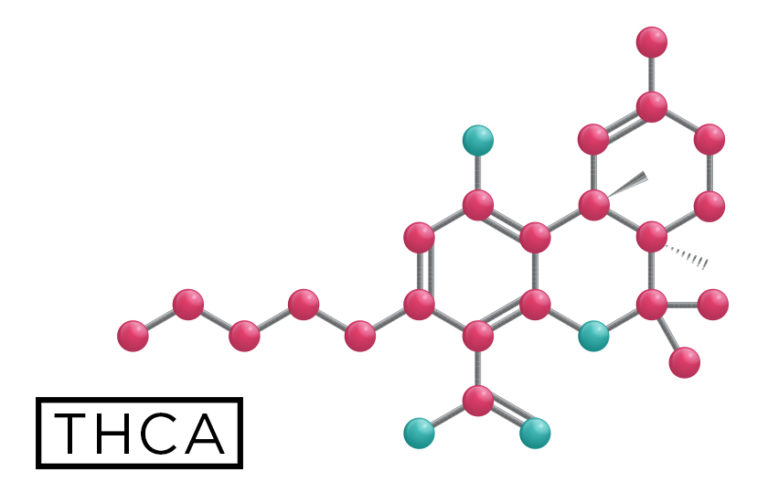
Image lightbox

What is THCA?
THCA is produced in trichomes, the tiny glandular hairs found across the surface of the cannabis plant. Trichomes are responsible for producing the cannabis plant's cannabinoids and terpenes. Trichomes contain resin glands that make the terpenes, THCA, and other phytocannabinoids.
Cannabinoids are produced in trichomes through biosynthesis, a process in which enzymes trigger a series of chemical reactions to make complex molecules out of smaller, simpler ones. The enzymes responsible for creating the cannabinoids with which most of us are familiar are cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) synthase, cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) synthase, and tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase. THCA synthase takes the central cannabinoid precursor CBGA and converts it into THCA, in addition to several other acidic cannabinoids.
THCA vs THC
The cannabis plant produces hundreds of cannabinoids, but only a few of them cause the euphoric high that is unique to cannabis. Most people assume that the cannabis plant produces THC during the growth period, when it is actually primarily producing the larger THCA molecule.
The main difference between THC and THCA is that THCA is not intoxicating, while THC is. THCA is the precursor that becomes THC when exposed to dryness or heat over a prolonged period of time. THCA from a raw cannabis plant won't make you feel high. This is why you can eat or drink the raw plant and not feel any intoxicating effects.
THCA converts into THC through decarboxylation, the process of heating a cannabinoid to the point of removing a carboxyl group. Decarboxylation enhances this cannabinoid's ability to interact with the body's cannabinoid receptors.
The THCA molecule doesn't produce intoxicating effects because it doesn't fit into the brain's cannabinoid receptors. THCA's shape is different than THC, due to an extra carboxyl group attached to the molecule. This carboxyl group is what makes THCA an acid. In fact, most cannabinoids (CBDA, CBGA, THCVA) take this acidic form when harvested, and it is only later that they become the cannabinoids we're more familiar with (CBD, CBG, THCV).
What's on the label?
At this point, you may be wondering how your dispensary-purchased cannabis flower is tested for THC potency if the THCA has not yet been decarboxylated. The THC amount you see on a label is actually a measurement of total potential decarboxylated THCA.
Is THCA illegal?
THCA is not scheduled at the federal level as a banned substance. It is possible, however, that THCA could be considered an analog of THC and possession of it could be prosecuted under the Federal Analogue Act. No sample of THCA is completely free of THC.
THCA effects and medical uses
THCA offers a range of useful medicinal applications. The therapeutic value of THCA has been somewhat overlooked in favor of cannabinoids such as THC and CBD. THCA benefits include anti-inflammatory, immunoregulatory, anti-tumor, neuroprotective, and anti-emetic properties.
THCA exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1, COX-2), and modulates immune activity through metabolic pathways other than CB1 and CB2. It can also act as a potent neuroprotectant by activating Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) pathways, and may, along with other non-THC
cannabinoids, inhibit prostate cancer growth
Mechanism of action
Without decarboxylation, THCA has very little affinity for the cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptor, and is therefore incapable of producing intoxication. Decarboxylation changes theshape of THCA, and the new shape (THC) fits the binding pocket of the CB1 receptor. These receptors are largely found in the central nervous system, where they regulate a wide variety of brain functions, and facilitate the intoxicating and pain-relieving effects of THC.
THCA is a highly unstable compound, which makes it difficult to observe and protect from THC contamination. Researchers have been able to observe, however, that THCA interacts with several receptor pathways other than CB1 and CB2, including COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) proteins, and the cytokine interleukin 10 (IL-10).
THCA products
Raw cannabis flower
Raw cannabis has massive potential as a superfood alongside avocados and kale. More consumers are looking for recipes to consume raw cannabis for the non-intoxicating, medicinal benefits of THCA.
Tea and topicals
Other popular non-activated, non-decarboxylated products include tea and topicals. Cannabis tea is typically not heated at high enough temperatures for THCA to decarboxylate into THC, making it a mildly-to-non-intoxicating substance that will appeal to those who drink tea for immunoregulatory and general medicinal purposes.
Topicals are cannabis-infused products applied directly to the skin for medicinal purposes, allowing for cannabinoids to be absorbed into the bloodstream at a slower rate than if cannabis were smoked or eaten. Similarly to cannabis tea, topicals can be a great choice for people who want relief without the full intoxicating effects. Topicals that include THC may prove mildly intoxicating, but only if THC reaches the bloodstream. And even then, this happens so slowly that most people don't detect any intoxication or psychoactivity. Topicals infused with THCA are non-intoxicating.
THCA oil
THCA is also available as an oil that can be consumed in a variety of ways. THCA oil requires the extraction of THCA at room temperature to ensure the molecule doesn't convert into THC. Over time, however, the THCA content becomes THC unless the product is stored at a very cold temperature. THCA oil can be used to ease physical discomfort and inflammation, stimulate appetite, and induce calming effects. THCA tinctures can be applied under the tongue or used as a spray.